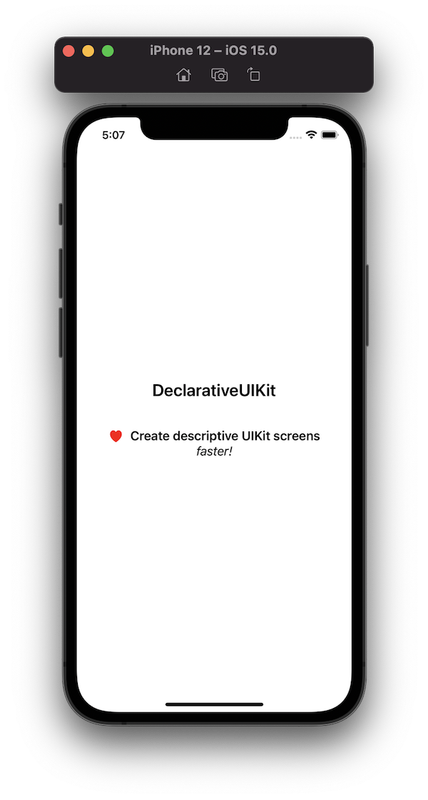
更快地创建描述性的 UIKit 屏幕!
摆脱约束操作,使用声明式语言来创建你的视图,从而减少 UI 代码,使视图更具可读性并加快迭代速度。
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
var body: UIView {
VerticalStack {
Spacer()
UILabel()
.text("DeclarativeUIKit")
.font(.boldSystemFont(ofSize: 24))
.padding(.bottom, 20)
HorizontalStack {
UIImageView()
.image(UIImage(systemName: "heart.fill")?.withTintColor(.red, renderingMode: .alwaysOriginal))
.padding(.trailing, 4)
UILabel()
.text("Create descriptive UIKit screens")
.font(.boldSystemFont(ofSize: 18))
}
UILabel()
.text("fast!")
.font(.italicSystemFont(ofSize: 18))
Spacer()
}
.alignment(.center)
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.backgroundColor = .white
// add is a convenience method that abstracts the work of
// setting `translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints` to false
// and connecting the content view with the superview.
// In other words, by calling `add` with `content`, it will expand the content to fit the view.
view.add(body)
}
}
- XCode 11.4+
- Swift 5.2+
- iOS 10+
- 更具可读性的代码
- 更少的代码行数
- 没有花哨的类,因此你不需要子类化或使用任何其他东西,只需使用纯粹的 UIKit 即可。
- 对众所周知的方法使用相同的命名,因此你可以跟随你的直觉。
让我们重新创建以下视图
使用 UIKit,它可能看起来像这样
class RegularAlarmCardView: UIView {
private let title: String
private let subtitle: String
init(title: String, subtitle: String) {
self.title = title
self.subtitle = subtitle
super.init(frame: .zero)
setupView()
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
func setupView() {
let imageView = UIImageView(image: UIImage(systemName: "alarm"))
let titleLabel = UILabel()
let descriptionLabel = UILabel()
imageView.contentMode = .scaleAspectFit
imageView.setContentHuggingPriority(.defaultHigh, for: .horizontal)
titleLabel.text = title
titleLabel.font = .boldSystemFont(ofSize: 14)
descriptionLabel.text = subtitle
descriptionLabel.font = .systemFont(ofSize: 12)
addSubview(imageView)
addSubview(titleLabel)
addSubview(descriptionLabel)
imageView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
titleLabel.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
descriptionLabel.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
imageView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeAreaLayoutGuide.topAnchor),
imageView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeAreaLayoutGuide.leadingAnchor, constant: 20)
])
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
titleLabel.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: imageView.safeAreaLayoutGuide.topAnchor),
titleLabel.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: imageView.safeAreaLayoutGuide.trailingAnchor, constant: 10),
titleLabel.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeAreaLayoutGuide.trailingAnchor)
])
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
descriptionLabel.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: titleLabel.safeAreaLayoutGuide.bottomAnchor),
descriptionLabel.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: titleLabel.safeAreaLayoutGuide.leadingAnchor),
descriptionLabel.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeAreaLayoutGuide.trailingAnchor),
descriptionLabel.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: safeAreaLayoutGuide.bottomAnchor)
])
}
}
通过使用 DeclarativeUIKit,我们可以简化这段代码
class DeclarativeAlarmCardView: UIView {
lazy var body: UIView = {
HorizontalStack {
UIImageView(image: UIImage(systemName: "alarm"))
.contentMode(.scaleAspectFit)
.set(contentHuggingPriority: .defaultHigh, for: .horizontal)
.padding(.leading, 20)
VerticalStack {
UILabel()
.text(title)
.font(.boldSystemFont(ofSize: 14))
UILabel()
.text(subtitle)
.font(.systemFont(ofSize: 12))
}
.padding(.leading, 10)
}
.alignment(.top)
}()
private let title: String
private let subtitle: String
init(title: String, subtitle: String) {
self.title = title
self.subtitle = subtitle
super.init(frame: .zero)
add(body)
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
}
这大约减少了原始视图设置代码 50% 的行数,而且我们不必处理任何约束。 最重要的是,这个框架最大的优势之一是它操作视图的容易程度。 重新定位元素就像交换元素一样容易,而不是手动连接受影响视图的相应约束。 此外,它的声明性质使得仅通过查看代码就可以轻松地可视化视图的组成,非常类似于 SwiftUI。
你的团队可能想要使用此框架的主要原因如下
- 它支持较旧的 iOS 版本 (iOS 10+)。
- 它比使用纯 UIKit 开发更快。
- 它比带有约束的纯 UIKit 更具可读性。
- DeclarativeUIKit 是一个很好的过渡到 SwiftUI 的工具,因为它借鉴了它的一些特性(例如声明式外观和 spacer 的使用),同时与 UIKit 元素完全兼容。
- 它比 SwiftUI 更容易掌握。
DeclarativeUIKit 是 UIKit 的扩展,而不是 SwiftUI 的替代品。 因此,在 UIKit 类中找到的 setter 将具有返回对象本身的对应项,同时尽可能保持相同的命名,这与 SwiftUI 的情况不同。 例如,当将 UIKit 视图的背景颜色设置为绿色时,我们调用 view.backgroundColor = .green。 此框架将为你提供一个具有相同名称的函数,view.backgroundColor(.green),这与 SwiftUI 不同,后者将是 view.background(Color.green)。 尽管我们尝试保持相同的名称,但在某些情况下这是不可能的,例如 addArrangedSubview 和其他一般方法。
DeclarativeUIKit 不会在幕后进行任何魔法,它只是抽象了约束的使用。 因此,自动布局规则在这里是相同的。 尽管如此,我们可能会借鉴 SwiftUI 的一些元素和概念,比如 Spacer,仅仅是因为 UIKit 中没有等效的东西,它让我们的生活更轻松。
import DeclarativeUIKit
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
var body: UIView = {
VerticalStack {
UILabel()
.text("Hello world!")
.font(.boldSystemFont(ofSize: 24))
.textAlignment(.center)
.textColor(.white)
}
}
}
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
var body: UIView = {
...
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.add(body)
}
}
Spacers 将尝试扩展,因此我们可以使用它来移动内容并允许某些区域增长,从而避免布局问题。
例如:将内容推到底部
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
var content: UIView = {
VerticalStack {
Spacer()
// Some Element here
}
}()
...
}
在 使用 Spacers 来移动内容 中查看更多内容。
与 SwiftUI 中一样,Spacers 会扩展并移动你的内容。
将内容推到右侧
HorizontalStack {
Spacer()
// Some Element here
}
将内容向上推
VerticallStack {
// Some Element here
Spacer()
}
居中内容
HorizontalStack{ //or VerticalStack()
Spacer()
// Some Element here
Spacer()
}
就像使用 Autolayout 时一样,如果未正确配置,你的视图可能会出现布局问题。 例如,如果你有一个连接到屏幕所有角的堆栈,然后你在其中插入两个标签,xcode 会抱怨高度歧义。
这是因为 xcode 必须扩展其中一个视图以适应屏幕,并且你还没有定义应该“破坏”哪个视图才能实现这一点。
使用 DeclarativeUIKit,有一些解决此问题的方法
- 设置内容拥抱优先级,就像你使用常规堆栈一样
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
lazy var body: UIView = {
VerticalStack {
UILabel()
.text("Title")
.set(huggingPriority: .defaultHigh, for: .vertical)
UILabel()
.text("Subtitle")
}
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.add(body).backgroundColor(.white)
}
}
- 使用 Spacer,以便它可以相应地扩展。
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
lazy var body: UIView = {
VerticalStack {
UILabel()
.text("Title")
UILabel()
.text("Subtitle")
Spacer()
}
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.add(body).backgroundColor(.white)
}
}
- 允许堆栈根据需要扩展,就像你通常所做的那样
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
lazy var content: UIView = {
VerticalStack{
...
}
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
content.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.backgroundColor(.white).addSubview(content)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
content.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.safeAreaLayoutGuide.topAnchor),
content.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.safeAreaLayoutGuide.leadingAnchor),
content.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.safeAreaLayoutGuide.trailingAnchor),
content.bottomAnchor.constraint(lessThanOrEqualTo: view.safeAreaLayoutGuide.bottomAnchor)
])
}
}
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
lazy var content: UIView = {
VerticalStack()
.addArranged(
titleLabel
)
.addArranged(
subtitleLabel
)
}()
var titleLabel = UILabel().text("Title")
var subtitleLabel = UILabel().text("Subtitle")
...
}
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
lazy var content: UIView = {
...
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.addSubview(content)
content
.backgroundColor(.white)
.connect(\.topAnchor, to: view.safeAreaLayoutGuide.topAnchor)
.connect(\.leadingAnchor, to: view.safeAreaLayoutGuide.leadingAnchor)
.connect(\.trailingAnchor, to: view.safeAreaLayoutGuide.trailingAnchor)
.connect(\.bottomAnchor, to: view.safeAreaLayoutGuide.bottomAnchor)
}
}
import UIKit
import DeclarativeUIKit
class DeclarativeViewController: UIViewController {
lazy var content: UIView = {
VerticalStack()
.addArranged(
UILabel().text("Title")
.set(\.heightAnchor, to: 50)
.set(\.widthAnchor, to: 100)
)
.addArranged(
UILabel().text("Subtitle")
.set(\.heightAnchor, to: 50)
)
.spacer()
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.add(content).backgroundColor(.white)
}
}
即使你的应用程序不支持 SwiftUI 或 iOS 13,你仍然可以利用预览 Canvas。 此功能未包含在此框架中,因为你可能必须向你的项目添加一些额外的标志。 但是,如果你仍然想使用它,这是你可以执行的操作
- 添加一个
UIViewControllerRepresentable作为容器
@available(iOS 13.0, *)
struct ViewControllerContainer: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
let viewController: () -> UIViewController
init(_ viewController: @escaping () -> UIViewController) {
self.viewController = viewController
}
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> some UIViewController {
viewController()
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIViewControllerType, context: Context) {}
}
- 在你的 View Controller 文件的底部添加一个预览
#if DEBUG
import SwiftUI
@available(iOS 13.0, *)
struct MyViewController_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
ViewControllerPreview {
MyViewController()
}
}
}
#endif