- FluidCore
- 一组实用工具
- FluidRuntime
- 一个运行时库,可启用隐藏的功能
- FluidGesture
- 使视图可拖动
- FluidKeyboardSupport
- 将键盘区域与视图内容集成
- FluidPictureInPicture
- FluidSnackbar
- FluidStack
- UINavigationController 的替代方案
- FluidStackRideauSupport
- FluidTooltipSupport
- 悬浮在特定点上的视图
- 显示具有触摸事件处理的任何目标图层
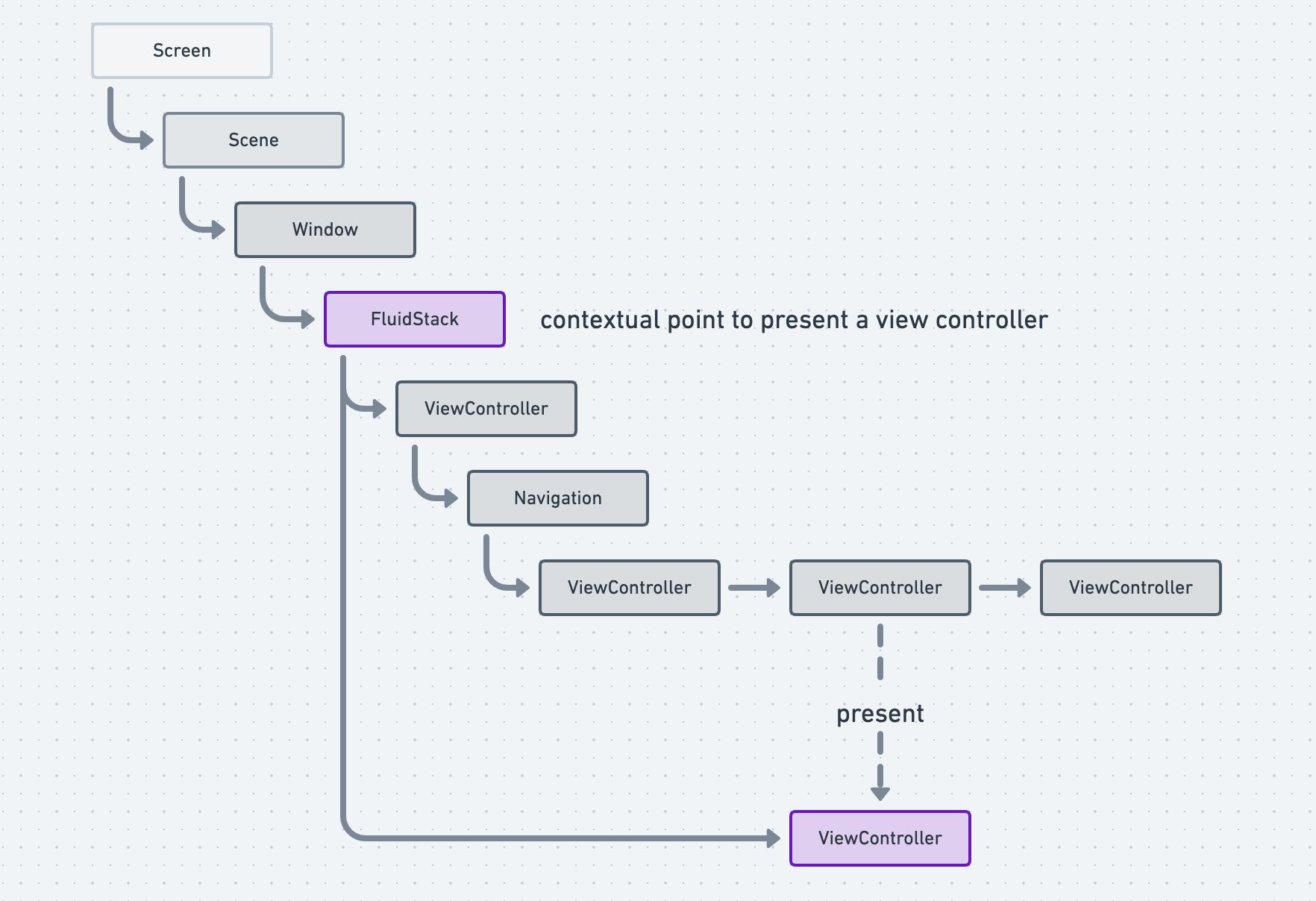
FluidStack 为您的 iPhone 应用程序提供高级的基础设施。
构建在 UIKit 之上,用自定义组件替换 UIKit 标准转换。
它提供的组件使您的应用程序更灵活 - 交互式和可中断的转换,可以自由地展开视图控制器,而无需 pop 或 dismiss。
这非常适合创建完全自定义的 UI 应用程序,例如 Snapchat、Zenly、Uber、Instagram Threads。
FluidInterfaceKit 的核心组件是 FluidStackController,它使用自定义转换堆叠视图控制器。
应用程序运行此组件,只是堆叠,但可以获得灵活性。
💔 请注意使用此框架的风险; 使用它的意义在于脱离 Apple 的 UIKit 生态系统。 例如:后退栏按钮的历史记录菜单、页面表单模态和辅助功能。 该框架会尝试尽可能地遵循 UIKit 的更新。
| 类似 Instagram Threads | 类似 Apple |
|---|---|
 |
 |
通常,UIKit 允许我们使用 UIViewController.present、UIViewController.dismiss、UINavigationController.push、UINavigationController.pop 来进行屏幕管理。
如果一个视图控制器需要在模态和导航上显示,则该视图控制器需要同时支持两者。
在模态中,如果它使用 navigationItem,则应该使用 UINavigationController 包装以显示。
此外,该视图控制器会考虑如何自行关闭,除非由外部处理。
Pop 还是 dismiss 取决于上下文。
FluidInterfaceKit 提供 FluidStackController,它类似于 UINavigationController。 它提供所有在堆叠中管理的视图控制器,作为堆栈的子级。
尝试想想如果我们正在使用 UINavigationController 会怎么样。
所有视图控制器都将在其上显示,并推送到下一个视图控制器,如果需要嵌套,则推送另一个 UINavigationController。
过渡的表达不是问题,我们可以创建一个自定义过渡,因此它可以像模态呈现 - 从底部滑入。
如果应用程序这样运行,我们只使用 push 和 pop 来管理屏幕,除非使用 present 的特殊情况 - UIAlertController 或第三方库中的其他模态。 然而,模态工作得很好,因为没有人使用 presentation。
如上所述,FluidStackController 类似于 UINavigationController,它只是堆叠作为子级管理的视图控制器。
与 UINavigationController 的区别在于过渡,它提供了创建自定义过渡的接口,并且支持更大的灵活性。
使用 UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning 运行的自定义过渡在模态呈现和推送过渡中存在一些限制。
它支持取消,这将是灵活性的一部分,但还不够。
请参阅 iOS 主屏幕中发生的情况,它支持完全响应用户交互 - 打开应用程序、通过主页栏取消打开、将主页移回,然后通过触摸再次打开应用程序。
此项目中的 ExampleApp 展示了如何设置。
FluidInterfaceKit-Demo 展示了许多示例。
首先,您需要在 UIWindow 的根视图控制器中放置一个 FluidStackController。
在基于 Storyboard 的应用程序中,将入口指向的视图控制器设置为 FluidStackController 或其子类。
在基于代码的应用程序中,将 UIWindow 的根视图控制器设置为 FluidStackController 或其子类。
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions 在 AppDelegate 中
let newWindow = UIWindow()
newWindow.rootViewController = RootViewController()
newWindow.makeKeyAndVisible()
window = newWindow
RootViewController
final class RootViewController: FluidViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.backgroundColor = .systemBackground
// 📍
addContentViewController(FirstViewController(), transition: .disabled)
}
}
FirstViewController
final class FirstViewController: FluidViewController {
func runSomething() {
fluidPush(SecondViewController(), target: .current, relation: .hierarchicalNavigation)
}
}
SecondViewController
要关闭自身,请调用 fluidPop()
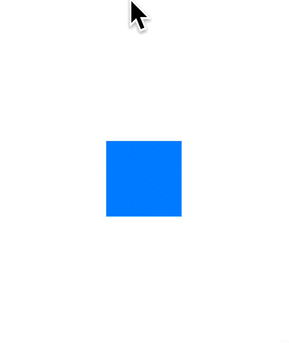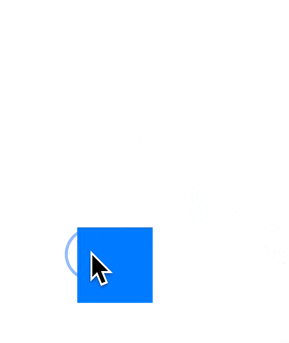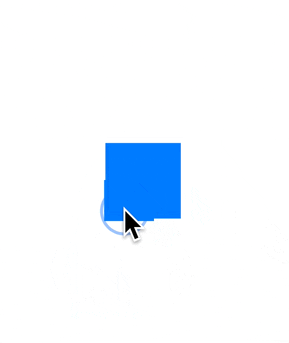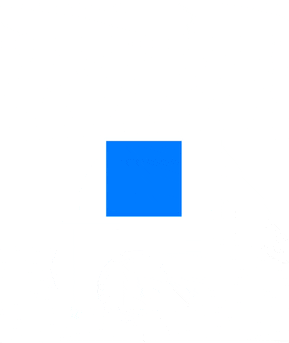
以一种更简单的方式使视图可以拖动。
支持拖动完成动画,通过弹簧动画使用尊重手势速度的移动到另一个位置。
内置了橡皮筋效应。
let draggableView: UIView
draggableView.makeDraggable(
descriptor: .init(
horizontal: .init(min: -200, max: 200, bandLength: 30),
vertical: .init(min: -200, max: 200, bandLength: 30),
handler: .init(
onStartDragging: {
},
onEndDragging: { velocity, offset, contentSize in
// return proposed offset to finish dragging
return .init(width: 0, height: 0)
}
)
)
)

如果您可以做出贡献,我将使用一次性赞助等级来赞助您。
- 改进核心组件
- 改进文档
- 增长演示应用程序