在代码中符合人体工程学地描述布局
🏗 结构化布局 API
Mondrian.buildSubviews(on: view) {
VStackBlock {
titleLabel
HStackBlock {
cancelButton
sendButton
}
}
.padding(24)
}
💃 为了保留 AutoLayout 的灵活性,我们提供了经典的 API 风格
经典布局 API
sendButton.mondrian.layout
.width(120)
.top(.toSuperview)
.trailing(.toSuperview)
.leading(.to(cancelButton).trailing)
.activate()

🤵🏻♂️💭 我们认为我们仍然没有涵盖所有使用场景。 请随时在 Issues 中提出您遇到的情况!
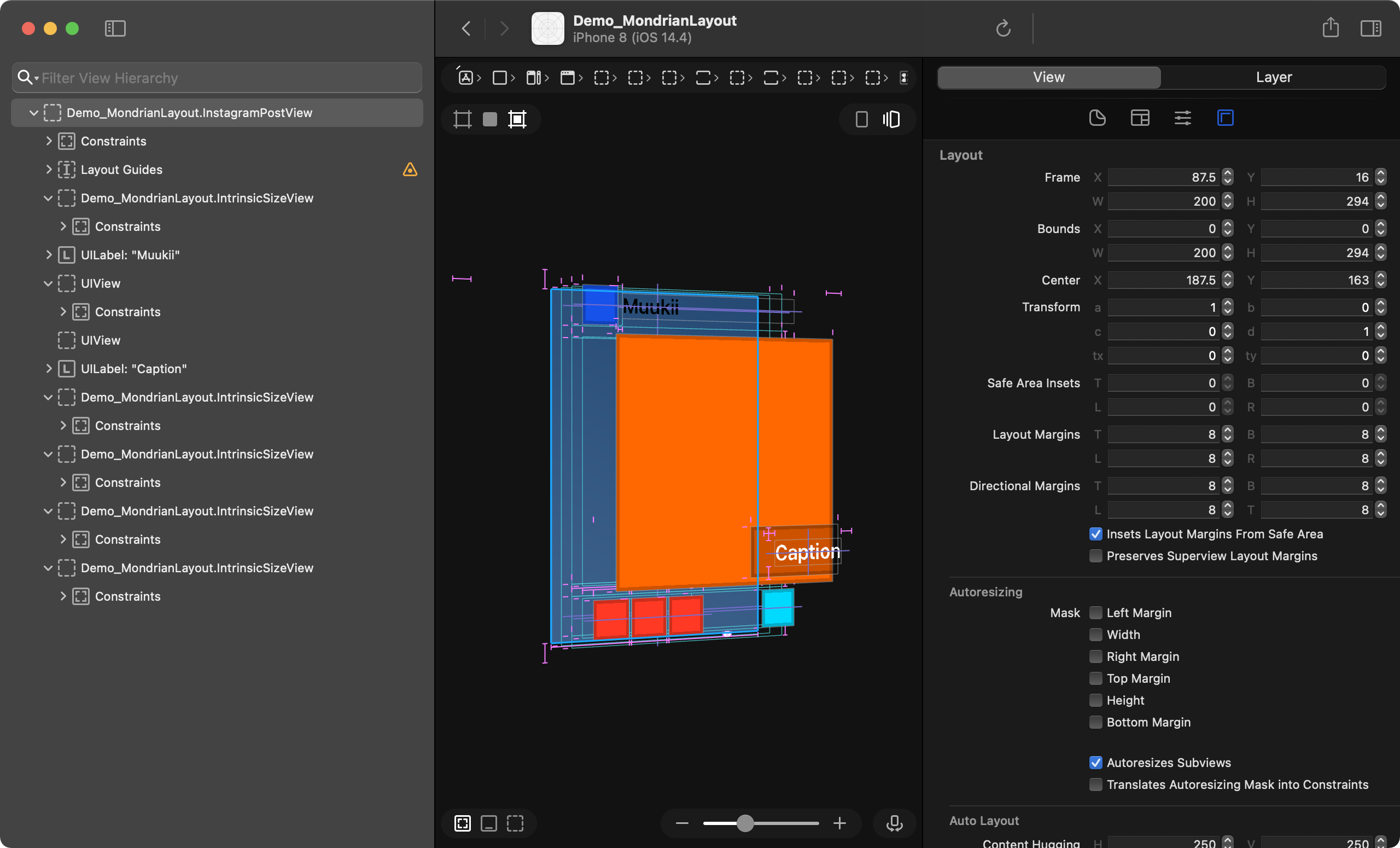
此图像由 MondrianLayout 布局
布局代码
HStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
VStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .mondrianRed,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 50)
)
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .mondrianYellow,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
HStackBlock(alignment: .fill) {
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
}
}
VStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
HStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
VStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
HStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .mondrianYellow,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
}
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
}
}
HStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
VStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .mondrianBlue,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
}
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
VStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
}
}
HStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .mondrianRed,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
VStackBlock(spacing: 2, alignment: .fill) {
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor,
preferredSize: .init(width: 28, height: 28)
)
}
}
}
}
.overlay(
UILabel.mockMultiline(text: "Mondrian Layout", textColor: .white)
.viewBlock
.padding(4)
.background(
UIView.mock(
backgroundColor: .layeringColor
)
.viewBlock
)
.relative(bottom: 8, right: 8)
)
- 🌟 符合人体工程学地支持我们通过 DSL(如 SwiftUI 的布局)描述布局。
- 🌟 根据布局表示自动添加子视图。
- 🌟 支持与系统 AutoLayout API 集成。
- 🌟 提供经典的布局 API,用于描述每个视图的约束。
基于 DSL 的 AutoLayout 布局构建器
AutoLayout 在描述布局以及它如何根据边界框变化方面非常强大。
如果我们能获得更符合人体工程学的接口来声明约束会怎样。
 |
 |
- 优化代码 - 实现仍然冗长,因为我们不确定 API 是否可以稳定。
- 完善 DSL - 在描述中保持稳定。
- 添加更多修饰符以进行布局微调。
- 调整堆栈块的行为。
- 除了 DSL 之外,还添加了一种独立设置约束的方法
- AutoLayout 绝对是描述布局的强大工具。 我们可能需要额外设置约束,因为 DSL 无法描述布局的每种模式。
您可以从演示应用程序中看到许多布局示例。
Simulator.Screen.Recording.-.iPhone.8.-.2021-06-20.at.02.48.38.mp4
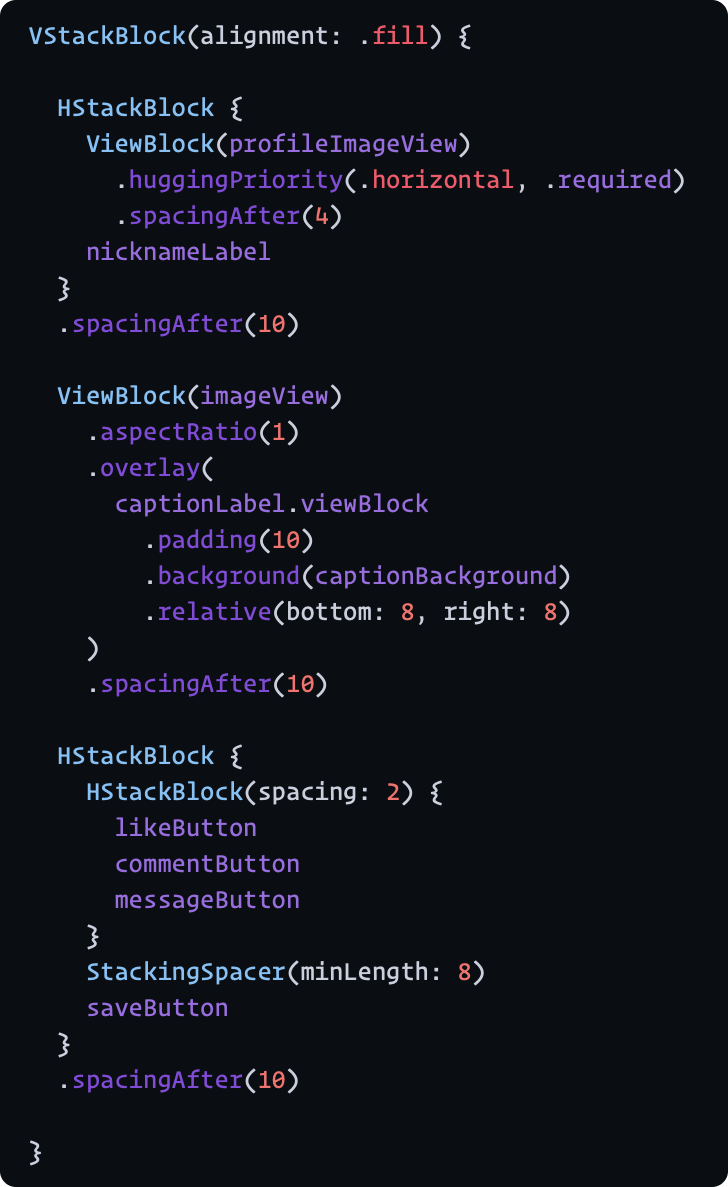
MondrianLayout 使我们能够通过 DSL(由 resultBuilders 提供支持)描述子视图的布局
它就像在 SwiftUI 中描述一样,但此行为略有不同,因为它是由 AutoLayout 系统布局的。
要描述布局,请使用 buildSubviews 作为入口点。
此方法创建一组 NSLayoutConstraint、UILayoutGuide 和 UIView 的修饰符。
最后,这些适用。 您不需要调用 addSubview。 这会根据布局描述的层次结构自动进行。
class MyView: UIView {
let nameLabel: UILabel
let detailLabel: UILabel
init() {
super.init(frame: .zero)
// Seting up constraints constraints, layoutGuides and adding subviews
Mondrian.buildSubviews(on: self) {
VStackBlock {
nameLabel
detailLabel
}
}
// Seting up constraints for the view itself.
Mondrian.layout {
self.mondrian.layout.width(200) // can be method cain.
}
}
}
示例代码假定在 UIView 中运行。(self 是 UIView)
您可以将其替换为 UIViewController.view。
附加到顶部和底部安全区域。
Mondrian.buildSubviews(on: self) {
LayoutContainer(attachedSafeAreaEdges: .vertical) {
VStackBlock {
...
}
}
}
或者
Mondrian.buildSubviews(on: self) {
VStackBlock {
...
}
.container(respectingSafeAreaEdges: .vertical)
}
Mondrian.buildSubviews(on: self) {
ZStackBlock {
backgroundView.viewBlock.relative(0)
}
}
同义词
ZStackBlock(alignment: .attach(.all)) {
backgroundView
}
ZStackBlock {
backgroundView.viewBlock.alignSelf(.attach(.all))
}
Mondrian.layout {
self.mondrian.layout.width(...).height(...)
}
或者
self.mondrian.layout.width(...).height(...).activate()
relative(0) 填充到 ZStackBlock 的边缘。
Mondrian.buildSubviews(on: self) {
ZStackBlock {
profileImageView.viewBlock.relative(0)
textOverlayView.viewBlock.relative(0)
}
}
ZStackBlock {
myLabel
.relative(.all, .min(20))
}
ZStackBlock {
ZStackBlock {
myLabel
}
.padding(20) /// a minimum padding for the label in the container
}
对齐
| center(默认) | leading | trailing | fill |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| center(默认) | top | bottom | fill |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Mondrian.buildSubviews(on: self) {
VStackBlock(spacing: 4, alignment: alignment) {
UILabel.mockMultiline(text: "Hello", textColor: .white)
.viewBlock
.padding(8)
.background(UIView.mock(backgroundColor: .mondrianYellow))
UILabel.mockMultiline(text: "Mondrian", textColor: .white)
.viewBlock
.padding(8)
.background(UIView.mock(backgroundColor: .mondrianRed))
UILabel.mockMultiline(text: "Layout!", textColor: .white)
.viewBlock
.padding(8)
.background(UIView.mock(backgroundColor: .mondrianBlue))
}
}
在堆叠布局块中添加一个空格。
label
.viewBlock // To enable view describes layout
.padding(8)
.background(backgroundView)
label
.viewBlock // To enable view describes layout
.padding(8)
.overlay(overlayView)
.relative 修饰符描述内容附加到带有填充的指定边缘。
未指定的边缘没有到边缘的约束。 因此,大小取决于固有内容大小。
您可以使用此修饰符将边缘固定为叠加内容。
ZStackBlock {
VStackBlock {
...
}
.relative(bottom: 8, right: 8)
}
.padding 修饰符与 .relative 相似,但有所不同。
不同之处在于,未指定的边缘以 0 填充固定到边缘。
ZStackBlock {
VStackBlock {
...
}
.padding(.horizontal, 10) // other edges work with 0 padding.
}
 |
 |
在 Z 轴上堆叠视图(在中心对齐)
ZStackBlock {
view1
view2
view3
}
将每个视图扩展到指定的边缘
ZStackBlock(alignment: .attach(.all)) {
view1
view2
view3
}
指定每个视图的对齐方式
ZStackBlock {
view1.viewBlock.alignSelf(.attach(.all))
view2.viewBlock.alignSelf(.attach([.top, .bottom]))
view3.viewBlock.alignSelf(.attach(.top))
}
LayoutManager 支持它。
如果我们需要根据某些条件(例如取决于特征)更改布局,则此对象可以帮助实现。
// TODO: #19
结构化布局 API(DSL)不涵盖所有使用场景。
有时我们仍然需要一种描述复杂布局约束的方法。
MondrianLayout 也提供它,就像其他 AutoLayout 库一样。
独立激活约束
view.mondrian.layout
.width(10)
.top(.toSuperview)
.right(.toSuperview)
.leading(.toSuperview)
.activate() // activate constraints and returns `ConstraintGroup`
批量布局**
// returns `ConstraintGroup`
Mondrian.layout {
box1.mondrian.layout
.top(.toSuperview)
.left(.toSuperview)
.right(.to(box2).left)
.bottom(.toSuperview)
box2.mondrian.layout
.top(.toSuperview.top, .exact(10))
.right(.toSuperview)
.bottom(.toSuperview)
}
view.layout.horizontal(.toSuperview, .exact(10))
view.layout.vertical(.toSuperview, .exact(10))
view.layout.edge(.toSuperview)
view.layout.edge(.to(myLayoutGuide))
CocoaPods
pod "MondrianLayout"
SwiftPM
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/muukii/MondrianLayout.git", exact: "<VERSION>")
]
MondrianLayout 在 MIT 许可证下发布。