👉 我建议您查看 Fluxus 的源代码。如果您这样做,您会意识到这仅仅是一种模式,而非框架。请仔细研究,您可以构建自己的 Vuex 风格的 SwiftUI 存储。
Fluxus 是 SwiftUI 的 Flux 模式实现,它取代了 MVC、MVVM、Viper 等模式。
- 将所有模型数据组织到一个存储中,并在视图中轻松访问。
- 使用 mutations 修改应用程序的状态。
- 使用 actions 执行异步操作。
- 尽可能保持您的模型和视图简单。
MacOS 10.14 或 10.15 上的 Xcode 11 Beta
在 Xcode 中,选择 File -> Swift Packages -> Add Package Dependency 并输入 此仓库的 URL。
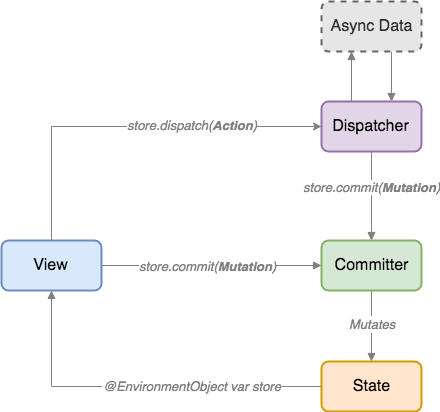
- 状态 (State) 是应用程序数据的根本来源。
- Mutations 描述了状态的同步更改。
- Committers 将 mutations 应用于状态。
- Actions 描述了异步操作。
- Dispatchers 执行异步操作并在完成后提交 mutations。
Fluxus 帮助我们处理共享状态管理,但代价是更多的概念和样板代码。如果您没有构建复杂的应用程序,并且直接使用 Fluxus,可能会觉得冗长而不必要。如果您的应用程序很简单,您可能不需要它。但是,一旦您的应用程序增长到一定复杂度,您将开始寻找组织共享状态的方法,而 Fluxus 可以为您提供帮助。引用 Redux 的作者 Dan Abramov 的话:
Flux 库就像眼镜:当你需要它们的时候,你就会知道。
使用 Fluxus 并不意味着您应该将所有状态都放在 Fluxus 中。 如果一段状态严格属于单个 View,那么仅使用本地 @State 就可以了。查看 landmarks 示例,了解本地 @State 和 Fluxus 状态如何协同工作。
- minimal example app 包含以下所有代码,是一个可以立即运行的示例。
- landmarks example app 是使用 fluxus 重新实现的官方 landmarks 教程应用程序。
- todo example app 是一个非常简单的待办事项列表实现。
状态是应用程序中模型数据的根本来源。我们创建一个状态模块,用于计数器,并将其添加到根状态结构中。
import Fluxus
struct CounterState: FluxState {
var count = 0
var myBoolValue = false
var countIsEven: Bool {
get {
return count % 2 == 0
}
}
func countIsDivisibleBy(_ by: Int) -> Bool {
return count % by == 0
}
}
struct RootState {
var counter = CounterState()
}
Mutations 描述了状态的更改。Committers 接收 mutations 并修改状态。
import Fluxus
enum CounterMutation: Mutation {
case Increment
case AddAmount(Int)
case SetMyBool(Bool)
}
struct CounterCommitter: Committer {
func commit(state: CounterState, mutation: CounterMutation) -> CounterState {
var state = state
switch mutation {
case .Increment:
state.count += 1
case .AddAmount(let amount):
state.count += amount
case .SetMyBool(let value):
state.myBoolValue = value
}
return state
}
}
Actions 描述了异步操作。Dispatchers 接收 actions,然后在操作完成后提交 mutations。
import Foundation
import Fluxus
enum CounterAction: Action {
case IncrementRandom
case IncrementRandomWithRange(Int)
}
struct CounterDispatcher: Dispatcher {
var commit: (Mutation) -> Void
func dispatch(action: CounterAction) {
switch action {
case .IncrementRandom:
IncrementRandom()
case .IncrementRandomWithRange(let range):
IncrementRandom(range: range)
}
}
func IncrementRandom(range: Int = 100) {
// Simulate API call that takes 150ms to complete
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + .milliseconds(150), execute: {
let exampleResultFromAsyncOperation = Int.random(in: 1..<range)
self.commit(CounterMutation.AddAmount(exampleResultFromAsyncOperation))
})
}
}
存储保存当前状态。它还提供 commit 和 dispatch 方法,这些方法将 mutations 和 actions 路由到正确的模块。
import SwiftUI
import Combine
import Fluxus
let rootStore = RootStore()
final class RootStore: BindableObject {
var didChange = PassthroughSubject<RootStore, Never>()
var state = RootState() {
didSet {
didChange.send(self)
}
}
func commit(_ mutation: Mutation) {
switch mutation {
case is CounterMutation:
state.counter = CounterCommitter().commit(state: self.state.counter, mutation: mutation as! CounterMutation)
default:
print("Unknown mutation type!")
}
}
func dispatch(_ action: Action) {
switch action {
case is CounterAction:
CounterDispatcher(commit: self.commit).dispatch(action: action as! CounterAction)
default:
print("Unknown action type!")
}
}
}
我们现在在 SceneDelegate.swift 内部将存储提供给我们的视图。
window.rootViewController = UIHostingController(rootView: ContentView().environmentObject(rootStore))
ContentView.swift
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView : View {
@EnvironmentObject var store: RootStore
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
Form {
// Read the count from the store, and use a getter function to decide color
Text("Count: \(store.state.counter.count)")
.color(store.state.counter.countIsDivisibleBy(3) ? .orange : .green)
Section {
// Commit a mutation without a param
Button(action: { self.store.commit(CounterMutation.Increment) }) {
Text("Increment")
}
// Commit a mutation with a param
Button(action: { self.store.commit(CounterMutation.AddAmount(5)) }) {
Text("Increment by amount (5)")
}
// Dispatch an action without a param
Button(action: { self.store.dispatch(CounterAction.IncrementRandom) }) {
Text("Increment random")
}
// Dispatch an action with a param
Button(action: { self.store.dispatch(CounterAction.IncrementRandomWithRange(20)) }) {
Text("Increment random with range (20)")
}
}
// Use with bindings
Toggle(isOn: myToggleBinding) {
Text("My boolean is: \(myToggleBinding.value ? "true" : "false")")
}
}.navigationBarTitle(Text("Fluxus Example"))
}
}
// Use computed properties to get/set state via a binding
var myToggleBinding = Binding<Bool> (
getValue: {
rootStore.state.counter.myBoolValue
},
setValue: { value in
rootStore.commit(CounterMutation.SetMyBool(value))
})
}
#if DEBUG
struct ContentView_Previews : PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
return ContentView().environmentObject(rootStore)
}
}
#endif
💡 您现在应该拥有一个应用程序,该应用程序演示了 Fluxus 和 SwiftUI 的 flux 模式的基础知识。如果您在运行此程序时遇到问题,请下载示例应用程序,或提交 Github 问题,我们会尽力提供帮助。
查看 landmarks example app,了解 fluxus 在更复杂的应用程序环境中的使用。
Swift/SourceKit 正在使用 100% 的 CPU!
这是 Xcode 11 beta 中的一个错误,它通常意味着您的 @EnvironmentObject 有问题,请确保您正确地将 .environmentObject() 传递给您的视图。
如果您要呈现一个新视图(例如模态窗口),您将必须将 .environmentObject(store) 传递给它,就像您的根视图控制器一样。
如果您发现错误或想到更好的方法,请提交问题。
在 Twitter 上关注我 @jsusek,了解有关 SwiftUI 的随机想法。